 Technology
Technology
- Insights
- Financial Services
- Article
Evolution of International Money Transfers: Challenges and Future Directions

Today, Swift transfers dominate the majority of cross-border, bank-facilitated foreign trade payments. However, this conventional method often results in long processing times, typically 1 to 4 days, and incurs significant commission fees. According to the World Bank, as of the fourth quarter of 2022, the average cost for bank transfers is 11.8% [1]. This figure underscores a stark reality: the high commission rates and time delays associated with traditional bank transfers seem increasingly antiquated in an era of digitalization. These costs disproportionately hit SMEs, which already operate on tight margins.
Complex Chain of Entities in Swift Money Transfer
Swift money transfers involve a chain of entities including the sender, recipient, the sender’s bank, the recipient’s bank, and sometimes intermediary or correspondent banks. As shown in the figure below, the process typically begins with the sender requesting the transfer from his bank and providing the required recipient information. If both the sender’s bank and the receiver’s bank are part of the same transfer network, the transaction can be executed directly between them. However, if these two banks do not have a direct connection, one or more intermediary banks step in to facilitate the transfer. In some cases, additional correspondent banks may be required for currency exchange purposes. It is important to note that each intermediary party in this chain takes a commission, which adds to the overall cost of the transaction.
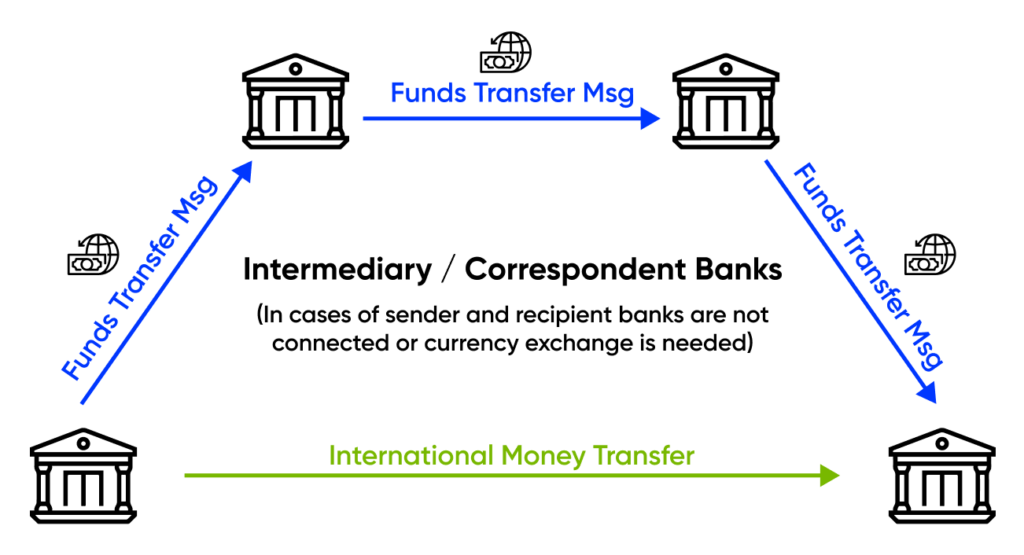
Figure 1 – The Chain of Entities Involved in Swift Money Transfer
Reasons for Delays in Money Transfers
During the transfer process, each participating bank engages in time-consuming regulatory processes and charges commissions, resulting in monetary and time costs for customers. Several factors contribute to potential delays in Swift money transfers, including the involvement of intermediaries, regulations, fraud controls, time zone & working time differences, currency conversions, and inaccuracies in payment details. Let us examine each one of these:
- Regulatory Requirements: One of the main reasons for delays in international wire transfers is banks’ strict adherence to anti-money laundering (AML), fraud prevention, and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. These regulatory checks must typically be performed at each intermediary / correspondent bank along the transfer route before the funds can proceed to the recipient bank. Furthermore, once the funds arrive at the recipient bank, additional procedures may be required. For instance, transfers exceeding certain amounts may need additional operational approval, and further investigations may take place if the transaction description contains specific keywords or if the country of origin is on the investigation list. All these investigations may further delay the payment process.
- Different Time Zones: Time zone differences between banks involved in the transfer process can cause delays, as transactions typically occur during standard business hours. If a transaction is routed to a bank in an Eastern time zone, operations may be deferred until the next business day.
- Holidays and Weekends: Holidays vary from country to country, and in some countries, Friday and Saturday are considered weekends. Similar to the effect of different time zones, the timing of transactions within the week or year can also cause delays.
- Currency Conversion: If the transfer requires a currency conversion, there may be additional steps and regulations that can cause additional delays. Certain currencies are subject to more regulations and government controls, which may cause additional delays. For example, a money transfer between two countries that do not transact in USD will require the use of a US correspondent bank, adding another layer of complexity and potential delay.
- Countries and Institutions Involved: Money transfers to some countries may require additional regulations, particularly due to sanctions, which may prevent transfers or cause further delays. Also, the efficiency of banking systems and connections play a crucial role in determining transfer speed. Countries with robust banking infrastructures and well-established connections tend to offer faster transfer services. Conversely, a lack of efficient banking systems and connections may contribute to delays in the transfer process.
- Inaccuracies in payment details: Money transfers require accurate payment details such as the name of the recipient, account number, bank name, and code. Any inaccuracies in this information can lead to delays or even necessitate the return of the payment.
The world is becoming increasingly interconnected and global trade activities are expanding daily. As globalization increases competition, the need for faster operations is becoming critical. To meet this growing need, disruptive money transfer technologies are rapidly emerging to provide quicker and more efficient transfer solutions.
Disruptive Technologies and Approaches for International Money Transfer
In recent years, the international money transfer landscape has evolved dramatically, driven by disruptive technologies and innovative approaches. These new methods offer faster, more cost-effective, and secure alternatives to traditional banking systems, meeting the needs of both individuals and businesses. Below, we explore some of the key technologies and platforms that are changing the way international money transfers are conducted.
- P2P Money Transfer Platforms: Platforms like PayPal, Venmo, or Square Cash offer faster, easier, and more predictable money transfer options with user-friendly interfaces. These peer-to-peer (P2P) payment platforms are designed for quick transfers, typically using authenticated accounts, phone numbers, or email addresses. They employ security protocols to protect transactions and user information. Payment is usually very fast, even spontaneous. Users typically register by providing their name, email, phone number, and some authentication details. Accounts created can be linked to bank accounts, credit cards, or debit cards. Many of these platforms also function as e-wallets. Money transfers can be initiated by choosing the recipient’s account or personal information and specifying the transfer amount. These platforms support multiple currencies and offer several advantages such as faster transfer times, lower commissions, and favorable exchange rates. However, they also come with limitations, including transaction limits, which may not be suitable for larger trade transactions. Additionally, they lack specialized trade finance services such as Letter of Credit or document collection, which are essential for secure money transfers in commercial transactions.
- E-Wallet: E-wallets are digital services that allow users to pay or transfer money online. They work much like debit or credit cards. Users can deposit money into their e-wallets or link them to existing bank accounts or credit cards. E-wallets enable almost instantaneous international money transfers, usually within minutes or hours, to the recipient’s digital wallet or bank account, subject to certain limits and international monetary regulations. They streamline the currency exchange process, reducing transaction costs and discrepancies in exchange rates. Utilizing encryption and verification technologies, e-wallets ensure secure transactions and protect sensitive financial information from fraudulent attempts.
However, e-wallets face challenges due to varying laws and regulations in different countries. B2B transfers can also be challenging because e-wallets are primarily designed for personal use and authentication methods are often inappropriate for business transactions. For B2B international money transfers, specialized e-wallet providers should be used to address the specific needs of business transactions.
- Virtual IBAN: Virtual IBAN (vIBAN) is a reference number for directing payments to a real bank account. Multiple numbers of vIBANs in different currencies can be linked to a single bank account. The vIBANs can be generated locally in the country where you want to receive money, regardless of the recipient’s residency status. For example, a customer in Germany can send money to a local vIBAN, and that amount is channeled to the physical bank account in Turkey. Digital money transfer platforms use vIBANs to provide fast and secure transactions, making cross-border transfers virtually indistinguishable from domestic ones. Importantly, each vIBAN remains linked to the main bank account in the home country, ensuring seamless integration. A unique vIBAN can be created for each customer group based on currency, customer region, and transaction type, typically at a lower cost than a traditional bank account. This approach enables faster international money transfer with lower commissions and streamlines the reconciliation process. However, incorrect recipient information can yield delays or cancellations of transfers, underscoring the importance and accuracy of transaction details.
- Multi-Currency Account: A multi-currency account is a single account that can hold, deposit, and transfer money in multiple currencies. These accounts are helpful for companies with international operations that have suppliers or customers in different currency zones and make frequent international transfers. They help international money transfers by eliminating the need for exchange currencies during transactions, thereby reducing associated fees and processing time. Also, usually, multiple currency accounts have additional services such as credit and debit cards with no transfer fees, making it easier to spend money abroad without incurring additional costs.
Compared to traditional banks, which usually charge higher rates, multi-currency accounts feature more competitive rates. Also, users can have better control over the potential negative effects of currency fluctuations during transactions. Furthermore, these accounts help companies simplify their reconciliation and accounting processes. However, despite their advantages, multi-currency accounts may have higher fees and lower interest rates compared to standard deposit accounts. That is why, it is more advantageous to utilize them primarily for transferring funds rather than for long-term storage.
- Fintechs with Letter of Credit and document collection services: Fintech companies are increasingly providing services comparable to traditional banking for foreign trade payment methods, such as Letter of Credit and Document Collection. These companies provide international B2B money transfers and guarantee that payments are made only when pre-agreed conditions are met. This saves time for both the importer and the exporter. This approach is particularly advantageous for SMEs, given the high rejection rates of letter of credit applications – up to 45% [2]. However, fintech providers need to further expand their network to provide a platform for more importers and exporters to meet.
- Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrency coins offer another avenue for international money transfers, enabling quick transactions from one country to another, often within minutes according to Statistica [3]. These coins can then be converted into local currency or used through various methods such as cryptocurrency-enabled cards, direct coin use, or crypto ATMs. Coins allow for fast international money transfers. Moreover, currency conversions are completely free or have minimal fees, mitigating the risk of encountering high exchange rates. However, for larger amounts, coins with high liquidity and backed by fiat money are beneficial for easy conversion to local money. Nevertheless, cryptocurrency to fiat money conversions can be flagged as suspicious by local banks, causing delays. Additionally, cryptocurrency coin transfers may face more AML regulations, so, on-ramp and off-ramp procedures should be checked.
What can banks do?
New money transfer methods are rapidly evolving to offer faster and more cost-effective solutions, though there is still room for improvement in AML controls and security measures. As regulatory bodies respond to these developments, we can expect to see new regulations such as enhanced KYC procedures for enterprise users engaging in B2B transfers. While such regulations may initially increase transfer times, they also have the potential to increase transfer limits, thereby enhancing the overall utility of these methods.
Besides, the introduction of new regulations will increase the trustworthiness of these money transfer methods, challenging the dominance of traditional banking systems. If banks fail to adapt their systems to emerging technologies and introduce services such as letters of credit or document collection, they risk not only losing transfer incomes but also customer churn. This is especially critical for SMEs, which already operate on tight margins and are increasingly focused on cost and time efficiency.
Banks are already taking steps to introduce faster and more predictable money transfer alternatives, such as Visa B2B, Mastercard Send, and Western Union. However, there is an urgent need for further improvements, including the adoption of even faster systems and participation in innovative money transfer networks. Fintech partnerships can help banks provide faster international money transfers by integrating e-wallet and money transfer platform services. Since innovative international money transfer solutions currently have lower zone coverage compared to traditional platforms, banks can focus on the countries where most money transfers take place. These integrations can create more user-friendly mediums for a seamless, more predictable customer experience with transparent pricing.
Banks can also adopt emerging technologies such as blockchain and distributed ledger systems through partnership integrations and by joining consortiums such as R3 and RippleNet. By building their own blockchain services, they can facilitate faster international payments and attract customers seeking more secure options. Additionally, blockchain technology enables innovative products such as smart contracts, which can be provided for trade finance.
Proactive preventive measures can be implemented by leveraging predictive analytics to identify potential threats, as demonstrated by Citibank and JPMorgan Chase. For example, JPMorgan Chase reduced false positives by 95% and improved accuracy by using machine learning to analyze customer data and detect potential risks. AI-driven automation of AML processes has also proven beneficial, with HSBC saving $400,000 annually by reducing the time required for reviews. Real-time monitoring and analysis by AI helped Danske Bank and Standard Chartered identify potential risks more effectively. Standard Chartered cut compliance review times by 40%, and Danske Bank reduced false positives by 60%, thereby enhancing the accuracy of their AML programs.
By adopting these advanced technologies and integrating them with existing banking services such as financing, guarantees, letters of credit, and document collection, banks can better compete with emerging money transfer technologies. This approach not only boosts customer satisfaction and operational efficiency but also prevents revenue leakage and increases overall profitability.
References
- World Bank Group. (2023, June 13) Remittances Remain Resilient but Likely to Slow. https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2023/06/13/remittances-remain-resilient-likely-to-slow
- Department of Finance. (2022). SME Credit Demand Survey – October 2021 – March 2022. https://assets.gov.ie/233991/210a2791-fb63-42e2-bb38-ffb81d4b82e4.pdf
- Average transaction speed of 74 cryptocurrencies with the highest market cap as of January 2024. (2024, January). https://www.statista.com/statistics/944355/cryptocurrency-transaction-speed/

Explore deep-dive content to help you stay informed and up to date
 Technology
Technology
 Financial Services
Financial Services
Revolutionizing Credit Cards: Tailored Solutions for Every Lifestyle
Read now Financial Services
Financial Services
Unleashing the power of content: Transforming banking with a content house
Read now Financial Services
Financial Services